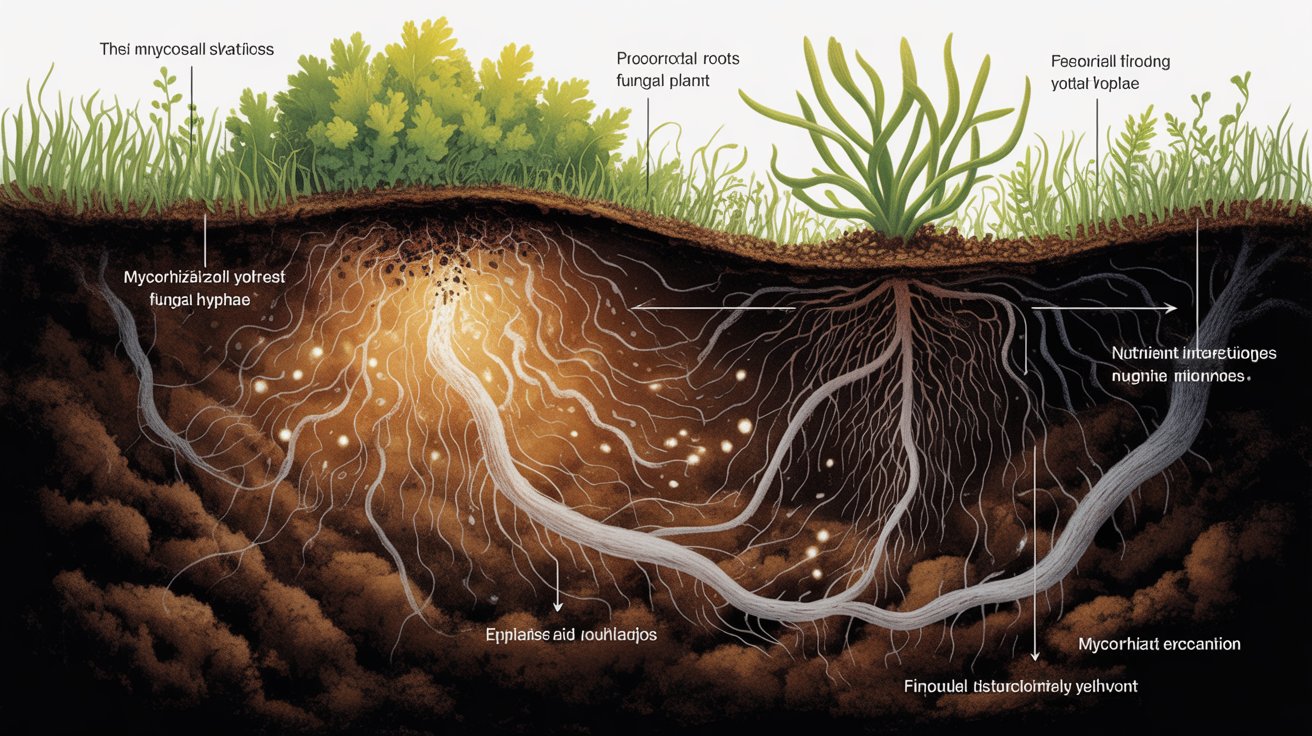
Mycorrhiza refers to a unique and symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots. This partnership plays a crucial role in enhancing plant health by facilitating nutrient and water absorption. In this relationship, the fungi extend the root system of the plants, forming a network that helps plants access essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, from the soil. The fungi, in turn, benefit from the carbohydrates produced by the plant through photosynthesis. This natural collaboration has been instrumental in the growth of plants for millions of years.
There are several types of mycorrhiza, each playing a specific role in nature. Arbuscular Mycorrhiza (AM) is the most common form, forming a deep connection with the plant’s root cells. Ectomycorrhiza (EM), typically found in trees, creates a protective sheath around the roots. Additionally, Orchid Mycorrhiza helps orchids grow by connecting them with the essential nutrients they need. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types helps in appreciating its impact on plant growth, agriculture, and the overall ecosystem.
What is Mycorrhiza and Its Types? Exploring the Different Forms of Mycorrhizal Associations
Mycorrhiza refers to the mutualistic relationship between fungi and plant roots. This symbiosis enables plants to absorb essential nutrients from the soil while providing the fungi with carbohydrates produced by the plants. Mycorrhizal associations are found in nearly all plants, playing a vital role in plant health, soil fertility, and ecosystem sustainability. The relationship is highly beneficial as it helps plants grow more efficiently, supports their defense mechanisms, and enhances soil structure. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types is key to appreciating its ecological importance and agricultural applications.
There are several types of mycorrhizal fungi, each playing a unique role in this fungal-plant partnership. Below, we explore the most common types of mycorrhizae: Arbuscular Mycorrhizae (AM), Ectomycorrhizae (EM), and Orchid Mycorrhizae, each with distinct characteristics and contributions to plant growth.
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae (AM) and Its Role in Nutrient Exchange
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae (AM) are the most widespread type of mycorrhiza, found in over 80% of plant species, including many agricultural crops. AM fungi form a partnership with plants that enhances their ability to absorb nutrients, especially phosphorus, which is often limited in soils.
Ectomycorrhizae (EM) and Their Contribution to Forest Ecosystems
Ectomycorrhizae (EM) fungi are primarily associated with trees, especially those in temperate and boreal forests. Unlike AM fungi, EM fungi surround the root tips with a protective sheath, forming a structure that prevents the direct entry of harmful microbes.
- Nutrient Cycling: EM fungi help in the breakdown of organic matter, which contributes to soil fertility and nutrient cycling in forest ecosystems.
- Protection Against Pathogens: By forming a physical barrier around the roots, EM fungi protect trees from harmful soil-borne pathogens.
- Water Efficiency: Similar to AM, EM fungi enhance water uptake by increasing root absorption capacity, which is particularly beneficial in dry environments
Orchid Mycorrhizae and Their Specialized Function in Orchids
Orchid Mycorrhizae are a specialized form of mycorrhizal fungi that form a unique relationship with orchids. Unlike other types of mycorrhiza, which help plants absorb nutrients, orchid mycorrhizae are primarily involved in seed germination.
- Seed Germination: Orchid seeds are very small and lack the nutrients required for germination. Orchid mycorrhizae supply the necessary nutrients to the seeds, enabling successful germination.
- Nutrient Transfer: Once germination occurs, the fungi continue to provide the orchid with nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Species-Specific Interaction: Orchid mycorrhizae are highly specific to individual orchid species, which means each orchid requires a unique type of fungus for its growth and development.
The Science Behind Mycorrhiza: How It Works and Its Role in Plant Health
Mycorrhiza refers to the symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots, where both organisms benefit from the association. Fungi provide plants with essential nutrients and water, while plants supply the fungi with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis. This intricate partnership has evolved over millions of years and plays a crucial role in plant health, soil fertility, and overall ecosystem function. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types is vital to appreciating how mycorrhizal networks influence plant growth and health.
In the world of agriculture, horticulture, and forestry, mycorrhizae are indispensable for improving soil conditions and promoting plant growth. By extending the root system, mycorrhizal fungi provide plants with access to nutrients that would otherwise be difficult to obtain. The association also improves soil structure, enhances plant resilience, and boosts productivity, making it an essential component of sustainable farming and ecosystem health.
How Mycorrhizae Enhance Soil Fertility
Mycorrhizae play a critical role in enhancing soil fertility by improving the soil's ability to retain and cycle nutrients. These fungi extend their hyphal networks into the soil, increasing the root surface area and enabling better nutrient absorption. This results in a significant improvement in nutrient availability for plants.
Nutrient Exchange Between Plants and Mycorrhizal Fungi
One of the key functions of mycorrhiza is nutrient exchange. The fungi form structures inside or around the plant roots that facilitate the exchange of essential nutrients. Through this partnership, the plants gain access to minerals that are otherwise hard to absorb, while the fungi benefit from carbohydrates that plants produce through photosynthesis.
The Role of Mycorrhizal Networks in Root Expansion
Mycorrhizal fungi play a pivotal role in expanding the root systems of plants. By forming extensive fungal networks, mycorrhizae extend the reach of plant roots into the soil, allowing them to access water and nutrients from a wider area. This extension of the root system provides plants with a competitive edge in nutrient acquisition, especially in areas where resources are scarce.
- Increased Root Surface Area: Mycorrhizal fungi increase the surface area of the plant's root system, making it more efficient at absorbing nutrients, particularly those that are difficult for plant roots to access directly.
- Improved Water Absorption: The mycelium extends the reach of plant roots into deeper soil layers, where water and nutrients may be more abundant. This is especially important in drought-prone areas.
- Support During Transplantation: Mycorrhizal networks help new plants establish roots more effectively, providing them with the nutrients and support they need during the early stages of growth.
The Role of Mycorrhiza in Sustainable Agriculture and Gardening Practices
Mycorrhiza plays a crucial role in sustainable agriculture and gardening by enhancing soil health, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers, and promoting natural plant growth. This mutualistic relationship between fungi and plant roots improves nutrient uptake, boosts plant resilience, and contributes to a healthier, more biodiverse ecosystem. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types is essential for maximizing the benefits of this natural partnership, whether in large-scale farming or small-scale gardening.
In sustainable agriculture, mycorrhiza is increasingly being used to reduce environmental impact and improve productivity without the excessive use of synthetic chemicals. By enhancing soil fertility and promoting plant health, mycorrhizal fungi offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional farming practices. From reducing chemical fertilizer dependency to improving organic farming practices, mycorrhiza is a key element of eco-friendly farming and gardening strategies.
Using Mycorrhiza to Reduce Chemical Fertilizer Dependency
One of the most significant advantages of mycorrhiza is its ability to reduce the dependency on chemical fertilizers. By forming a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, mycorrhizae enhance nutrient uptake, particularly for essential elements like phosphorus, nitrogen, and other micronutrients. This naturally boosts soil fertility, enabling plants to thrive without the need for excessive chemical inputs.
- Improved Soil Health: Chemical fertilizers can degrade soil structure and harm beneficial microbes. Mycorrhizae, on the other hand, improve soil fertility without causing harm to the ecosystem.
- Lower Environmental Impact: Reducing the use of chemical fertilizers minimizes soil and water pollution, making farming practices more sustainable.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, farmers can save on input costs while promoting more natural soil fertility.
How Mycorrhiza Improves Organic Farming Practices
In organic farming, the use of synthetic chemicals is prohibited, making it essential to focus on natural methods to enhance soil fertility and plant health. Mycorrhiza is particularly valuable in organic farming because it boosts nutrient availability and enhances plant growth without the need for synthetic inputs.
- Enhanced Nutrient Availability: Mycorrhizal fungi help break down organic matter and make nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium more available to plants, which is especially important in organic farming where chemical fertilizers are not used.
- Improved Plant Resilience: Mycorrhizae increase plant resistance to stress factors such as drought, pests, and diseases, which are common challenges in organic farming.
- Soil Structure and Health: Mycorrhizal networks improve soil structure by binding soil particles together, leading to better water retention and aeration, which is essential for plant root development in organic systems.
Mycorrhiza's Role in Enhancing Crop Yields Naturally
The role of mycorrhiza in enhancing crop yields naturally is well-documented. These fungi improve nutrient absorption, water uptake, and plant growth, leading to stronger, more productive plants. Mycorrhizal fungi also improve soil structure and contribute to the long-term sustainability of agricultural land by increasing biodiversity and enhancing nutrient cycling.
How Mycorrhizal Fungi Help Combat Climate Change
Mycorrhiza plays a vital role in combating climate change by promoting carbon sequestration and improving soil health. This symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots has far-reaching environmental benefits that contribute to both mitigating and adapting to climate change. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types helps to uncover how these natural processes can be leveraged to reduce atmospheric carbon levels and enhance the resilience of ecosystems.
Mycorrhizal fungi are essential in maintaining healthy soil ecosystems, improving plant productivity, and supporting biodiversity. These fungi enhance plants' ability to absorb nutrients, water, and carbon from the soil, thereby facilitating carbon storage. By expanding the root systems of plants, mycorrhiza increases the volume of soil available for carbon absorption, making it a critical component of nature-based solutions to climate change.
Mycorrhizal Fungi and Carbon Sequestration
One of the most significant ways mycorrhiza helps combat climate change is through carbon sequestration. Mycorrhizal fungi capture carbon from the atmosphere and store it in the soil in the form of organic matter. The fungi convert the carbon into a stable form by integrating it into soil particles and plant roots, which can remain sequestered for long periods, often decades or more.
- Carbon Fixation: Mycorrhizal fungi assist plants in fixing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which is then transferred to the soil.
- Long-Term Carbon Storage: Carbon stored by fungi in soil organic matter is less likely to be released back into the atmosphere, making it a stable form of sequestration.
- Soil Structure Enhancement: The fungal networks also improve soil structure, helping retain carbon within the soil by preventing erosion and promoting soil aggregation.
Nature-Based Solutions to Climate Change with Mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza is a prime example of a nature-based solution to climate change, as it uses natural processes to address environmental challenges. These fungi enhance plant growth and carbon sequestration in a sustainable way, reducing the need for synthetic chemicals and high-energy inputs that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Enhancing Soil Carbon Storage Through Mycorrhizal Symbiosis
The mycorrhizal symbiosis between fungi and plant roots significantly enhances soil carbon storage by increasing the amount of carbon that can be retained in the soil. The network of fungal hyphae forms a vast subterranean network that connects plants and soil, facilitating the transfer of carbon and other nutrients. This symbiotic relationship is particularly important in improving soil structure and increasing organic matter retention in the soil.
- Increased Root and Fungal Biomass: The presence of mycorrhizae increases the root biomass of plants, which results in more organic matter being deposited in the soil, thus enhancing carbon storage.
- Carbon Stabilization: The fungi help stabilize organic carbon by binding it to soil particles, preventing the carbon from being released back into the atmosphere.
- Soil Aggregation: The hyphal networks also contribute to soil aggregation, improving soil structure and reducing the risk of carbon loss due to erosion.
Mycorrhiza in Action: Harnessing Its Power for Your Garden or Farm
Mycorrhiza plays a crucial role in enhancing soil health, promoting plant growth, and supporting sustainable farming practices. These beneficial fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, improving nutrient uptake, water absorption, and resistance to environmental stresses. Understanding what mycorrhiza is and its types can help you harness its potential in your garden or farm, ultimately leading to healthier plants and more productive harvests.
In both gardening and large-scale farming, mycorrhizal fungi can be used to optimize plant health and soil fertility. By promoting a natural, biological approach to soil management, mycorrhiza reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Whether you are growing vegetables in your backyard garden or cultivating crops on your farm, integrating mycorrhiza into your practices can lead to long-term improvements in soil structure, plant health, and yield.
Using Mycorrhizal Inoculants for Soil Health Improvement
Mycorrhizal inoculants are a powerful tool for improving soil health. These are products that contain live mycorrhizal fungi spores, which are added to the soil to establish the beneficial symbiotic relationship between the fungi and plant roots. What is mycorrhiza in this context? It's the introduction of these fungi to the soil environment to enhance nutrient cycling, improve soil structure, and increase the bioavailability of essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Improved Nutrient Uptake: Mycorrhizae help plants access nutrients that would otherwise be unavailable, particularly in nutrient-depleted soils.
- Enhanced Soil Structure: The fungal networks improve soil aggregation, which leads to better water retention, aeration, and reduced soil erosion.
- Increased Organic Matter Decomposition: Mycorrhizal fungi aid in breaking down organic matter, releasing nutrients into the soil that are essential for plant growth.
By using mycorrhizal inoculants, you can jump-start the process of improving soil health, especially in new or degraded soils. This natural approach reduces the need for chemical soil amendments, promoting a more sustainable gardening or farming practice.
Incorporating Mycorrhiza Into Your Farming Practices
Incorporating mycorrhiza into your farming practices is an effective way to boost soil fertility, enhance plant growth, and reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers. Mycorrhiza supports the establishment of healthy root systems, enabling plants to thrive with minimal external inputs. This symbiotic relationship is especially important for farmers looking to improve soil sustainability and increase crop productivity without harming the environment.
Integrating mycorrhiza into your farm’s soil management practices helps build long-term soil health, reduces input costs, and promotes a healthier, more productive crop yield.
Promoting Soil Microbes and Plant Resilience with Mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza not only benefits plants by improving nutrient and water uptake, but it also promotes a healthy soil microbiome, which is essential for long-term soil fertility and plant resilience. These fungi create a network of hyphae that interact with other beneficial soil microbes, helping to establish a balanced, thriving ecosystem within the soil.
- Microbial Diversity: Mycorrhizal networks support the growth of other beneficial microbes, such as bacteria that fix nitrogen and break down organic matter, further improving soil health.
- Increased Plant Resilience: The presence of mycorrhiza enhances a plant’s ability to withstand environmental stresses, such as drought, extreme temperatures, and soil-borne diseases.
- Soil pH Regulation: Mycorrhizal fungi help stabilize soil pH by interacting with soil minerals, making nutrients more accessible to plants and maintaining a balanced growing environment.
By promoting a diverse population of soil microbes and strengthening plant resilience, mycorrhiza plays a key role in creating robust and sustainable farming systems. The fungi ensure that plants have the support they need to grow healthily, even in challenging environmental conditions.
The Future of Mycorrhiza in Environmental Conservation
Mycorrhiza plays a pivotal role in environmental conservation, offering valuable solutions to some of the most pressing ecological challenges, such as biodiversity loss, soil erosion, and land degradation. These fungi form a vital symbiotic relationship with plant roots, promoting plant health, improving soil quality, and contributing to ecosystem resilience. Understanding what is mycorrhiza and its types can help harness the full potential of mycorrhizal fungi in conservation efforts, ensuring sustainable management of ecosystems and supporting long-term environmental restoration.
In environmental conservation, mycorrhiza is being recognized for its ability to enhance biodiversity, prevent soil erosion, and restore degraded lands. These benefits make mycorrhizal fungi a valuable tool in creating healthier ecosystems and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By supporting plant growth, improving soil structure, and facilitating nutrient cycling, mycorrhiza is contributing to a more sustainable and resilient environment for future generations.
Mycorrhiza and Biodiversity Conservation
Mycorrhiza plays a crucial role in biodiversity conservation by supporting plant species diversity and ecosystem stability. Fungal networks, established through the symbiotic relationship between plants and mycorrhizal fungi, help plants access essential nutrients and improve their growth. This, in turn, fosters a healthier and more diverse plant community, which supports a wide variety of animal species, from insects to larger herbivores.
- Plant Health and Growth: Mycorrhizal fungi provide plants with the nutrients they need to thrive, promoting stronger, healthier plants that are more capable of withstanding environmental stress.
- Supporting Diverse Plant Species: The enhanced nutrient uptake facilitated by mycorrhiza supports a wide variety of plant species, promoting plant diversity in natural habitats and agricultural systems.
- Ecosystem Stability: Healthy plant communities, supported by mycorrhizal fungi, form the foundation of stable ecosystems. A diverse range of plant species ensures that ecosystems are resilient to changes in climate or land use.
By maintaining healthy plant populations and enhancing soil fertility, mycorrhiza helps conserve biodiversity in both natural and managed ecosystems.
Mycorrhizal Networks and Soil Erosion Prevention
Mycorrhizal fungi contribute significantly to the prevention of soil erosion by improving soil structure and promoting root stability. The extensive networks of fungal hyphae that form within the soil help bind soil particles together, reducing soil loss due to wind and water. These fungal networks play an important role in preventing soil erosion, particularly in areas that are prone to degradation.
By promoting root growth and improving soil structure, mycorrhiza plays a vital role in mitigating soil erosion, helping to preserve topsoil and protect landscapes from degradation.
The Role of Mycorrhiza in Restoration of Degraded Lands
Mycorrhiza is an essential tool in the restoration of degraded lands, helping to restore soil fertility, promote plant growth, and rebuild ecosystem functions. Degraded lands, whether due to deforestation, overgrazing, or industrial pollution, often lack the nutrients and microbial life necessary for healthy plant growth. Mycorrhizal fungi can help revitalize these lands by improving soil structure and enhancing nutrient availability, paving the way for the re-establishment of natural vegetation.
- Soil Fertility Restoration: Mycorrhizal fungi enhance nutrient cycling in the soil, making nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen more available to plants. This helps restore soil fertility, which is often depleted in degraded lands.
- Plant Re-establishment: By forming symbiotic relationships with plant roots, mycorrhizae promote the successful establishment of plants, even in nutrient-poor or disturbed soils.
- Ecosystem Recovery: Healthy plant growth, supported by mycorrhizal fungi, is crucial for ecosystem recovery. Plants contribute to soil stabilization, water retention, and carbon sequestration, all of which are essential for ecosystem restoration.
By improving soil conditions and supporting plant establishment, mycorrhiza aids in the rehabilitation of degraded lands, contributing to the restoration of natural ecosystems and promoting sustainable land use practices.
FAQs
Q1. What is Mycorrhiza?
Mycorrhiza refers to a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots, where both organisms benefit. The fungi assist plants in nutrient and water absorption, while the plants provide the fungi with carbohydrates.
Q2. What are the Types of Mycorrhiza?
There are several types of mycorrhizae, including Arbuscular Mycorrhiza (AM), Ectomycorrhiza (EM), and Orchid Mycorrhiza. Each type has a specific role, such as nutrient exchange or supporting seed germination in orchids.
Q3. How Does Mycorrhiza Benefit Plants?
Mycorrhiza helps plants by improving nutrient uptake, especially phosphorus and nitrogen, enhancing water absorption, increasing resistance to stress, and promoting root development.
Q4. Can Mycorrhizae Be Used in Organic Farming?
Yes, mycorrhizae are ideal for organic farming as they reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, improve soil health, and promote sustainable plant growth.
Q5. How Can I Use Mycorrhiza in My Garden?
You can use mycorrhiza in your garden by applying mycorrhizal inoculants to the soil, coating seeds, or dipping plant roots in the fungi to enhance growth and improve soil health.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Mycorrhizal Networks for a Greener Future
Mycorrhizal networks play a vital role in fostering healthier, more sustainable ecosystems. By facilitating nutrient exchange, improving soil health, and promoting plant resilience, mycorrhizae are indispensable to both agriculture and natural ecosystems. Embracing the power of these fungal networks not only supports healthier plants but also contributes to carbon sequestration, reduced chemical dependency, and enhanced biodiversity.
As we continue to face environmental challenges, leveraging the benefits of mycorrhiza offers a natural, sustainable solution for improving soil fertility, combating climate change, and promoting ecological balance. By incorporating mycorrhizal fungi into farming, gardening, and conservation practices, we can pave the way for a greener, more resilient future.